Using real data lends credibility and accountability, however Synthetic data offers scalability, speed and privacy. Hybrid approaches leverage the best of both worlds, that provides the highest level of performance on multiple levels of use cases.
Contents
- What is real data?
- What is synthetic data? How is it generated?
- Real data: Pros and cons for model training
- Pros and cons of synthetic datasets
- Synthetic vs. real data: A detailed comparison
- When you should use real data
- When you should use synthetic data
- The hybrid approach: Best of both worlds
- Key challenges companies face when choosing data types
- Best practices for using real and synthetic data together
- Final verdict: Which is better for model training?
AI and Machine Learning (ML) models depend purely on their training data to understand the world, their tasks and perform. Studies show that 85% of AI initiatives have failed primarily because of the lack of sufficient quality and quantity of training data.
The quality, quantity and representativeness of training data directly influences every single predictive and classifying decision made by AI/ML models. Yet real data is often very costly, labor intensive and heavily restricted by regulations.
A viable alternative exists through synthetic data generation, which can create training data at scale, simulating those events or scenarios where data is scarce or has legal issues. These are the reasons why industry experts expect synthetic data to become the major source of training data for AI and ML models by 2030. For AI and ML companies balancing the use of both synthetic and real data for model development, the choice of which type of data to use has a big impact on the model’s performance and project timeline.
Making a real vs synthetic data comparison provides companies the ability to create robust AI model training datasets that meet their technical and operational requirements.
What is real data?
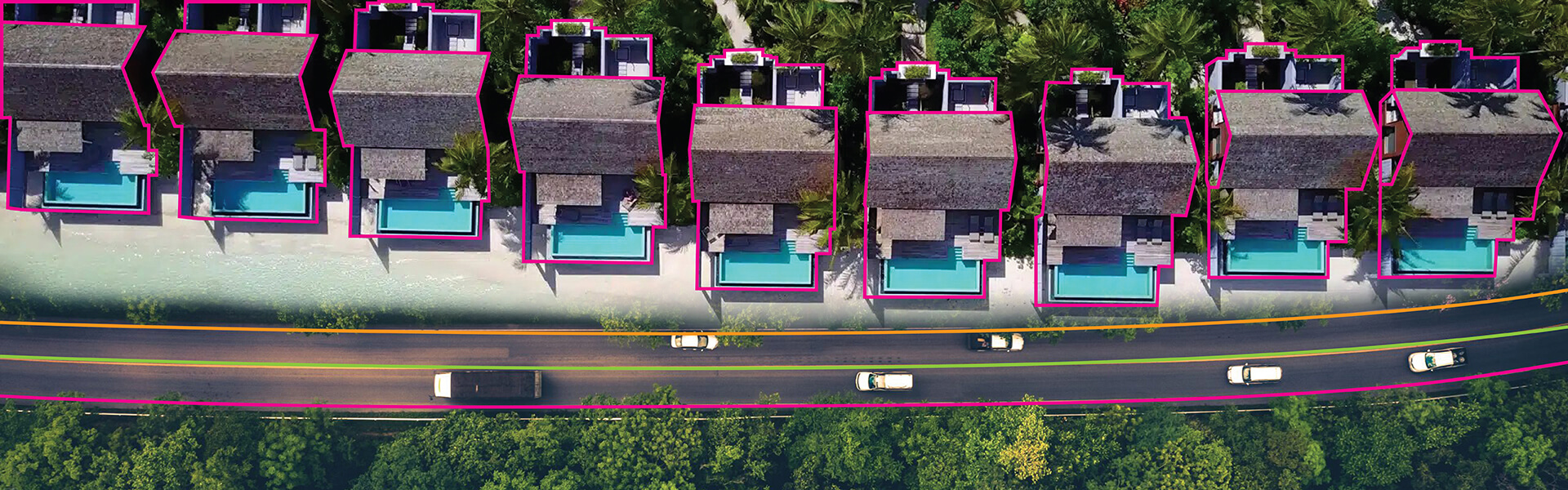
Data that actually occurs in a company’s operations or in real-life cases, and has been collected via its IOT sensors, customer transaction records, e-commerce product catalogs, medical imaging devices, video feed or licenses. Real data, as a result of being based on actual occurrences, can be complex and varied with regards to what may occur at any given moment in a business operation.
There is no better source when accuracy is concerned than using real word data for AI training. Models are able to learn how to recognize and understand all the small nuances that exist in your production environment by using real data.
However, there are some downsides to using real world data to train AI models. The most common are excessive noise present in the data, compliance issues that limit the types of data that organizations can use, lack of sufficient data to create a model and the tremendous cost of manually labeling the data. These can take up a considerable amount of the time and money spent in a project.
What is synthetic data? How is it generated?
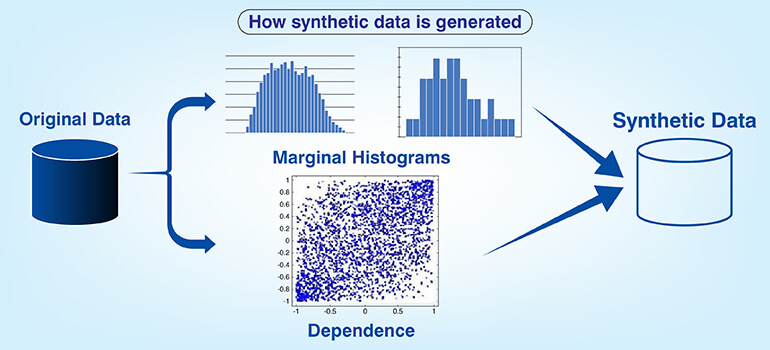
Synthetic data is artificially created using computer algorithms as opposed to capturing through observation. The statistical features of real world data are emulated in these data sets so that no reference exists to a specific individual or event.
Synthetic data generation techniques include Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), which use two competing neural nets and diffusion models that reverse the addition of noise into data sets. Rule based simulators also help in creating this data.
Generative AI datasets create edge cases, balance class distributions, generate compliant training examples for privacy concerns and provides statistically similar data to the original data set.
Generate synthetic text data to train NLP models at scale.
Create text data »Real data: Pros and cons for model training
There are both good points and disadvantages to utilizing real data. But keep in mind that some advantages have high costs associated with them.
Advantages of real data
- You get real data only from actual production environments and thus it is grounded in truth. Its authenticity is much higher than simulated data.
- Simulation may not fully capture the biological and operational complexities in safety critical applications such as autonomous driving and healthcare diagnostics.
- Real data pros include capturing the true behavior of users in e-commerce and fraud detection, which cannot be easily replicated through simulation.
- The key benefit of real data is the unreplaceable relationship between the real world and the true values in those worlds.
Limitations of real data
- Costs of real data collection are extremely high. For example, cost of sensors, data pipelines, data storage, etc.
- Large amounts of time required for label generation, requiring domain expert reviews of thousands of samples.
- Data collection and processing restrictions due to privacy and compliance concerns (e.g. GDPR, CCPA).
- Real data cons also include difficulty in capturing rare events and edge cases.
Pros and cons of synthetic datasets
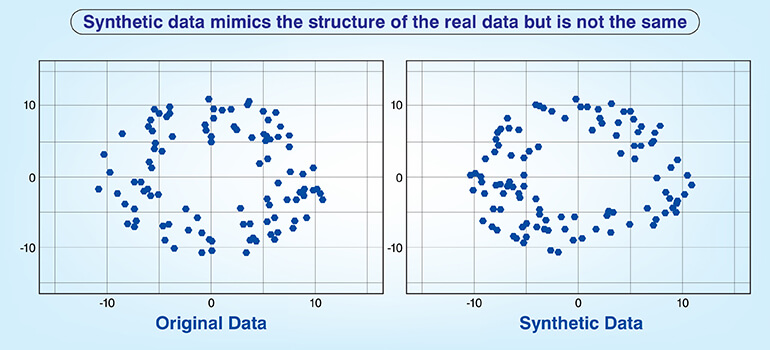
Synthetic data offers advantages when it comes to scalability and privacy. However it requires a well designed process for both generating and validating data.
Advantages of synthetic data
- A scalable solution that can produce millions of samples in just hours once you have developed an effective mechanism for synthesizing data.
- Does away with the complexities of working through a privacy workflow because privacy in synthetic data is based upon how it was generated.
- Synthetic data excels at data augmentation and simulating rare events by creating edge case examples, which appear too rarely in the actual data collected.
- Additional synthetic data pros include having the ability to precisely control the composition of the dataset to target known gaps.
Limitations of synthetic data
- Generating synthetic data requires significant domain expertise and can be difficult to avoid bias, even at a subtle level.
- Model training can lead to models that fit the synthetic data artifacts rather than fitting the generalized features of the real world data if the distribution of the synthetic data differs from the real world distribution.
- To accurately create synthetic environments, a significant amount of time, effort and cost must be invested prior to commencing the model training process.
- Synthetic data cons include the possibility of generating confident predictions that are wrong due to mismatch between the synthetic data and the production data distribution.
Create compliant synthetic data for regulated industries.
Contact our experts »Synthetic vs. real data: A detailed comparison
This chart shows how real data and synthetic data compare in terms of key factors that impact the decisions made about model training as well as the overall performance.
| Criterion | Real data | Synthetic data |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy |
Captures authentic patterns and real world complexity |
Depends on generation quality; may miss subtle correlations |
| Cost |
High collection and labeling expenses |
Lower after generation infrastructure established |
| Scalability |
Limited by collection speed and access |
Rapidly scalable through computational generation |
| Bias risk |
Reflects existing biases in collection processes |
Can introduce or amplify bias through generation assumptions |
| Privacy and compliance |
Requires extensive anonymization and regulatory controls |
Minimal privacy concerns when properly generated |
| Use case applicability |
Essential for safety critical and high fidelity applications |
Effective for augmentation, edge cases and privacy sensitive domains |
| Labeling effort |
Significant manual annotation required |
Labels generated automatically during synthesis |
| Availability of rare events |
Difficult to capture; requires extended collection periods |
Can be generated on demand for specific scenarios |
When you should use real data
The training data accuracy is directly related to the authenticity and true representation of the environment being modeled through its observation.
Real data use cases:
- Healthcare: Medical imaging and laboratory test results are used for diagnostics, therefore, diagnostic models need access to accurate clinical data to identify an illness.
- Fraud detection systems: These need to be trained on real world fraud attacks and real transactions to identify how fraudsters can adapt their tactics and how legitimate users may behave.
- User behavior prediction: Social and psychological factors in e-commerce, content recommendation and financial planning need to include models which represent all aspects of user behavior decisions.
- Financial market models: Historical trading data, price movements and economic indicators need to be included in the training data to make predictions about market trends and support investor decision making.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) models: Linguistic evolution and contextual usage for sentiment analysis and intent classification require ongoing training with authentic conversational data.
When you should use synthetic data
Choosing between real and synthetic data is dependent upon the frequency of occurrence of an event, as well as what level of privacy is required.
Ideal uses for the creation of synthetic data:
- Autonomous driving: Edge case autonomous vehicle training on synthetic data annotations for example, pedestrians crossing the roadway unexpectedly, vehicles running red lights and failures of equipment.
- Industrial defect detection: Such algorithms are trained by generating a variety of failure types and severity levels at different locations without having to wait for natural occurring defects.
- Robotic simulations: Developing algorithms for manipulating objects without having to physically utilize a robot for every iteration of training.
- Insurance anomaly detection: Anomaly detection of insurance claims and identification of rare medical conditions that have the least number of events of occurrence.
- Privacy restricted environments: Utilizing synthetic electronic health record and synthetic financial transaction data for compliant collaborative development.
The hybrid approach: Best of both worlds
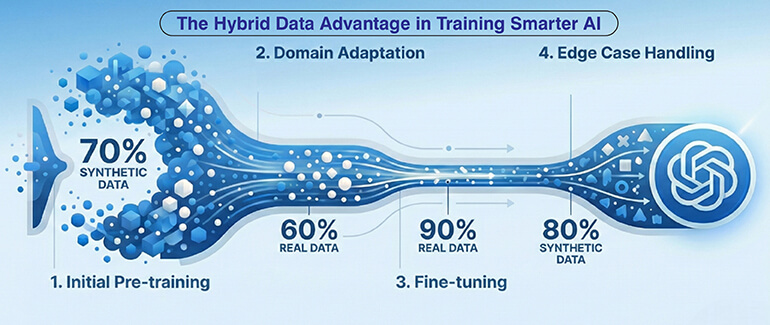
The majority of organizations are taking a hybrid strategy using a combination of synthetic data and real data to capitalize on their individual strengths. This trend is growing rapidly as besides using real world data, 75% of all organizations are expected to utilize generative techniques for synthetic data augmentation by 2026.
In the context of autonomous vehicle perception systems, an example of this hybrid strategy would be that the team trains on real driving footage which captures the actual patterns of traffic, weather and road infrastructure.
Once they have trained on real data, they then augment the training set with synthetic scenarios that demonstrate rare critical events (i.e., pedestrians suddenly stepping into highway lanes, multiple vehicles colliding, etc.) along with extreme weather combinations.
Real data provides the model with knowledge of normal driving environments, whereas the synthetic data exposes the model to the edge cases that are too difficult or expensive to collect naturally.
Training on a hybrid dataset allows for the development of more accurate models by allowing them to see numerous examples of the complete range of possible scenarios. The value of a hybrid dataset is reflected in the market where model training represents 45.3% of all global synthetic data use cases.
A staged training approach illustrates how the proportion of real versus synthetic data used in each phase of training can be optimized based upon the objective of the training phase.
| Training Phase | Data Type | Purpose | Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial pre training |
Synthetic (70%) |
Build foundational feature extraction and pattern recognition |
Rapid scaling with diverse scenarios |
| Domain adaptation |
Real (60%) + Synthetic (40%) |
Align learned features to production distributions |
Balance authenticity with coverage |
| Fine tuning |
Real (90%) + Synthetic (10%) |
Refine decision boundaries for deployment environment |
Maximize real world accuracy |
| Edge case handling |
Synthetic (80%) + Real (20%) |
Address rare events and failure modes |
Improve robustness without waiting for natural occurrences |
Key challenges companies face when choosing data types
Organizations that are making decisions about what types of data to use face a number of issues that require structured approaches and specialized knowledge of their domains.
These challenges include:
- Establishing appropriate measures of data quality to assess the representative nature, the coverage or scope of the data and the fidelity or completeness of the data collected from both real and synthetic data sets.
- Avoiding the amplification of bias due to either how the data was collected or how the synthetic data is assumed to be generated as required by fairness audits.
- Validating generated synthetic sample data to ensure it is representative of the domain using subject matter experts for domain accuracy.
- Weighing the cost of real data collection versus the engineering time required to build accurate synthetic data generation systems.
Best practices for using real and synthetic data together
Hybrid models need to be rigorously validated and governed so that each type of data contributes appropriately to overall model performance.
Best practices for combining types of data:
- Synthetic data should be used to pretrain a model and then fine tuned on a small sample of real world data.
- Data augmentation should be done in such a way that it maintains the same statistical distribution as found in production but does not distort the underlying structure of the data.
- Held out real data should be used during all phases of training to monitor for divergence between synthetic vs real world benchmarks.
- Data governance and quality frameworks should be established to document the methods used to generate synthetic data, quality standards for labeled data and the procedures to validate the use of the data.
- Performance of the model should be monitored continuously. When changes are detected which have shifted from those in the training data this should trigger a review to determine if updates are needed to the model.
- Partnerships with domain specialized providers can help ensure that the labeled datasets for ML models meets the required quality standards.
Final verdict: Which is better for model training?
There is no definitive superiority in real data or synthetic data and the choice of data depends upon the needs of your use cases, the size of your data sets and any regulatory constraints you may be subject to. While safety critical applications are primarily supported by predominantly real data due to cost concerns, privacy sensitive applications can leverage the scalability of synthetic data generation.
A hybrid approach is often the most useful method of using data for model development. It also offers an organization the flexibility to evolve with advancements in synthetic data generation techniques.
Accelerate AI deployment with domain ready datasets.
Get in touch today »
HabileData is a global provider of data management and business process outsourcing solutions, empowering enterprises with over 25 years of industry expertise. Alongside our core offerings - data processing, digitization, and document management - we’re at the forefront of AI enablement services. We support machine learning initiatives through high-quality data annotation, image labeling, and data aggregation, ensuring AI models are trained with precision and scale. From real estate and ITES to retail and Ecommerce, our content reflects real-world knowledge gained from delivering scalable, human-in-the-loop data services to clients worldwide.