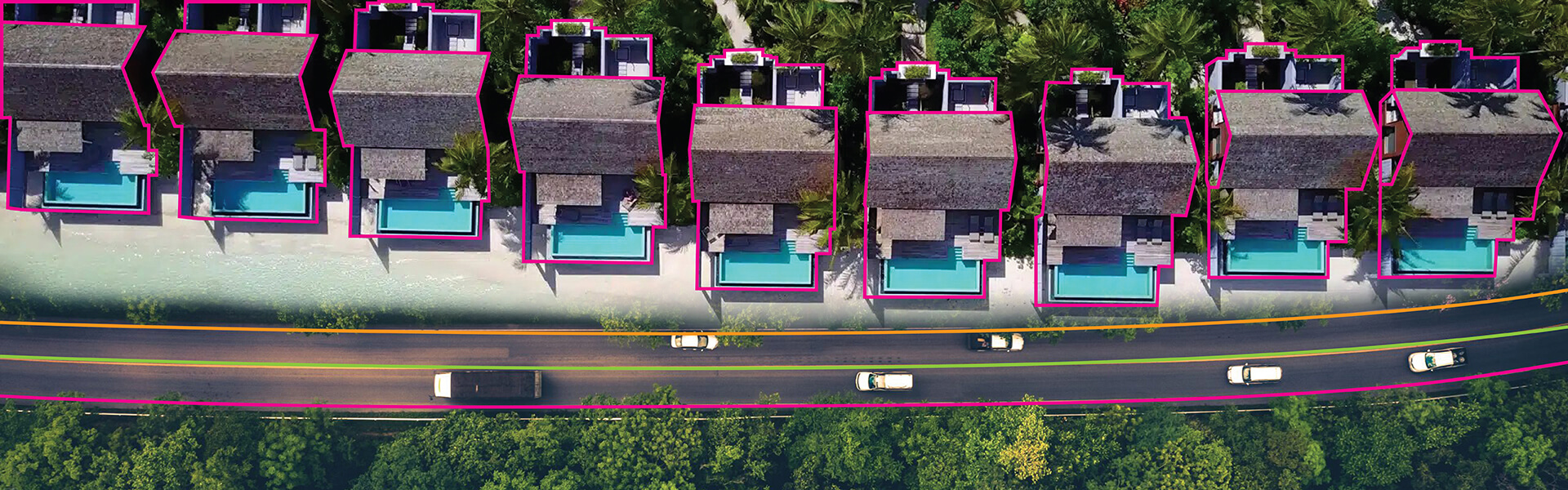
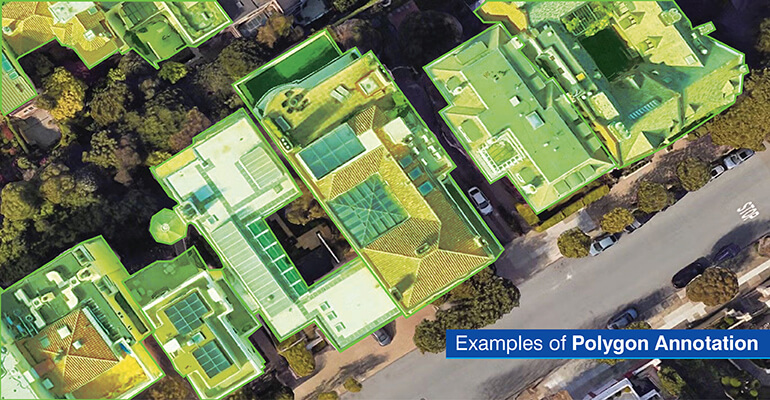
Polygon annotation is ideal for area based objects of complex shapes to delineate the boundary for image segmentation tasks. Polylines are better suited for linear structure or path detection. The decision of which one to use is based upon an object’s geometry, model needs and resource limitations.
Contents
- Why annotation techniques matter in high precision AI models
- What is polygon annotation?
- What is polyline annotation?
- Polygon vs. polyline annotation: A side by side comparison
- How the choice impacts your AI model performance
- How to choose between polygon and polyline annotation
- The role of quality assurance in polygon & polyline annotation
- Common mistakes teams make when choosing between polygon and polyline annotation
- Conclusion
To train computer vision models accurately to detect and segment objects, it is necessary to use the appropriate annotation techniques. Teams developing datasets for autonomous driving, medical imaging and industrial inspection often face a foundational decision, whether to use polygon annotation or polyline annotation.
The decision is significant as studies have demonstrated that poor quality annotations such as inaccurately defined boundaries can reduce model tracking accuracy by up to 18.4% which disables even the most robust algorithms.
Polygons and polylines capture object information in different ways thereby impacting labeling efficiency, model accuracy and overall inference performance. Polygon annotation in computer vision excel in defining area-based objects of irregular shape, while polylines are particularly well suited for capturing linear structures such as roads and pipelines.
By understanding the differences between polygon and polyline, you can decide on your annotation strategy to best fit the specific requirements of your models.
Why annotation techniques matter in high precision AI models
The precision of your training data is what will limit how well your model performs. Your annotation techniques for object boundaries will determine how your model interprets the visual information in those images. Precise object boundary labeling translate into better intersection over union (IOU) metrics and reliable predictions.
There are several ways to encode geometric information when using different computer vision annotation formats. For example, polygons are used to define enclosed regions for area based applications while polylines are used to capture the directional path of linear structures.
Inaccurate boundaries or misformatting of an annotation creates “noise” in the training signal. That noise can decrease the model’s ability to generalize across thousands of images.
What is polygon annotation?

Polygon annotation determines how the edges of objects are created. Industry studies have shown that polygon annotations produce 15-30% higher mask IoU (Intersection Over Union) than traditional bounding box annotations. This increase in precision is important as applications like defect detection or clinical diagnosis are highly sensitive to single-pixel errors.
Since each vertex of the polygon represents where the edge of the object changes direction, annotators need to select points on the edge of the object at those locations. Once they have selected all the necessary points, the tool will create lines between those points to create a multi-sided polygon that accurately reflects the true shape of the object.
This object shape annotation method allows annotators to add as many vertices as they feel is necessary to define the curves, protrusions and other details of the object.
Because polygons are closed boundaries, it is easy to determine which pixels are inside the object versus outside the object by simply determining if the pixel lies within the boundaries of the polygon. This allows for pixel-level classification for segmentation annotation methods.
When polygon annotation is used (use cases)
- Semantic segmentation projects: Polygon annotation is used as a reference point in computer vision to enable the classification of each pixel in an image.
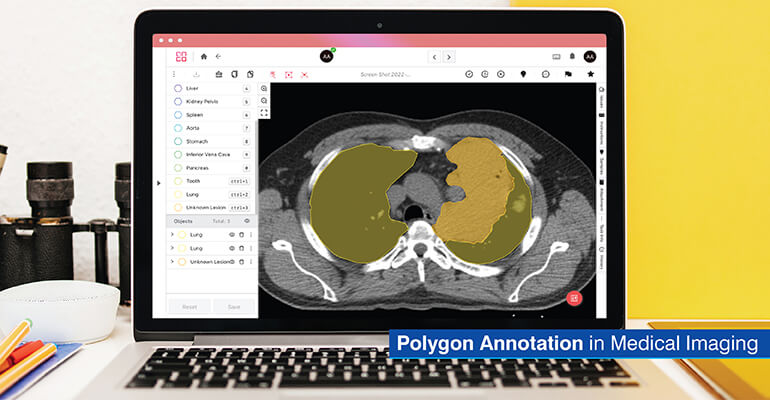
- Medical imaging: The boundaries of tumors, organs and tissues are annotated with respect to diagnostic models, where the impact of instance segmentation annotation on patient treatment is substantial.
- E-commerce platforms: Product isolation from background for virtual try-on functionalities and auto catalog Generation capabilities.
- Autonomous driving: Define pedestrians, vehicles, obstacles for collision avoidance purposes, which requires a full understanding of object shapes.
- Satellite imagery analysis: Segmentation of buildings, agricultural lands and land usage for mapping applications.
- Robotics applications: Train manipulation systems to be able to grasp non standard shaped objects in manufacturing and warehouse environments.
Precisely outline complex objects with polygon annotation services.
Talk to annotation team »Pros and cons of polygon annotation
Following are some of the pros and cons of using polygon annotation:
Pros
- Higher precision capturing object boundaries with pixel level accuracy
- Supports any object shape from organic forms to angular parts
- Essential for dense scenes where objects overlap
- Ideal for area based segmentation tasks
Cons
- Time intensive requiring significant annotation effort
- Higher labeling costs per image
- Requires skilled annotators for consistency
- Complex objects need dozens of vertices
What is polyline annotation?
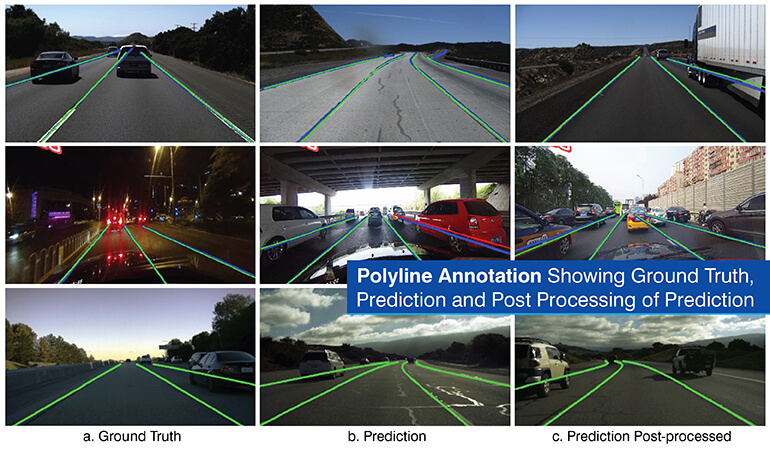
The polyline annotation method is an efficient method of identifying and marking linear features and paths. A polyline is made up of multiple connected lines created by placing sequential points along a linear feature. A polyline will not have the last point connect back to the first point of the polyline.
Polyline annotation use cases require identification of objects where the object’s width is less important than the path taken or the object’s direction. Because polyline annotations do not create an enclosed area, polyline for lane detection is much easier to compute.
The polyline annotation method is especially good at creating accurate annotations for small structures. For example, if a power line was hundreds of feet long and only a few pixels thick, it would be easy to identify using polyline annotation.
When polyline annotation is used (use cases)

- Autonomous driving lane detection: By polyline representation of a lane, the vehicle identifies the roadway structure and remain inside its designated lane.
- Infrastructure mapping: Aerial imagery is used to map edge of roadways, pipeline routes and detect wires or cables for automated maintenance plan process.
- Medical imaging: Blood vessels, nerves and lymphatic pathways are identified and modeled via polylines to provide three-dimensional views of a patient’s anatomy.
- Pose estimation: Systems that model a skeleton using polylines to connect joints and determine the orientation of limbs for motion analysis purposes.
- Agricultural monitoring: Irrigation channels and drainage pattern identification in field images for precision agriculture applications.
Build high-quality linear datasets for mapping and navigation models.
Explore polyline service »Pros and cons of polyline annotation
Following are some of the pros and cons of using polyline annotation:
Pros
- Faster labeling with fewer vertices required
- Lightweight datasets requiring less storage
- Ideal for thin and linear objects
- Efficient for path and trajectory prediction
Cons
- Not suitable for area based segmentation
- Cannot generate pixel wise masks
- Lower detail than polygons
- Limited to linear structure representation
Polygon vs. polyline annotation: A side by side comparison
For teams to make informed choices about labeling strategy, it is helpful to understand the similarities and differences between these annotation techniques for object boundaries.
| Criterion | Polygon Annotation | Polyline Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| Object Type |
Area based objects with well defined boundaries (vehicles, people, products, tumors) |
Structures and paths that are linear (lanes, roads, vessels, wires, skeletons) |
| Complexity |
High, requires multiple vertices to define shape details and curves |
Low, uses less than half points to draw linear paths or centerlines |
| Annotation Time |
Longer, complex objects may require 20 to 50 vertices per instance |
Faster, linear objects typically need 5 to 15 vertices |
| Accuracy Level |
Pixel level precision for boundary detection and segmentation |
Centerline and path level accuracy without width information |
| Cost |
Higher due to time investment and need for skilled annotators |
Lower due to faster labeling and simpler geometric requirements |
| Model Performance Impact |
Enables high IoU scores in segmentation tasks. Critical for boundary dependent applications |
Improves path prediction and directional detection. Essential for trajectory based tasks |
As shown above, there is a correlation between choosing the right annotation format based upon the properties of the method and the needs of your specific application. As the data annotation industry grows to be worth $17.37 billion by 2034, primarily due to the demand for complex computer vision in both healthcare and automotive industries, selecting the most suitable annotation method is a decision that can be valued into millions of dollars for AI leaders.
How the choice impacts your AI model performance
The type of data that is annotated will influence what your model learns and how well it will perform when deployed. Differences between polygon and polyline impact training dynamics, inference speed and prediction accuracy.
Impact on training speed & dataset size
Polygon annotation is converted to a segmentation mask which can be binary or multi-class array where each pixel gets a label. For example, a 1920×1080 image may have over 2 million pixel labels for every object in the segmentation mask.
Polyline annotation is exported as a list of coordinates with tens of values for an annotation whether high resolution or low resolution.
These size differences carry through the entire training pipeline. Smaller datasets take less time to load and use less memory and disk space.
Training with larger polygon labeling datasets requires more computational resources than training with polyline labeled datasets which can slow down iteration time while developing your product.
Impact on accuracy & model generalization
The use of polygons for tumor identification empowers the model to achieve higher intersection over union score (IOU) as it receives and uses that complete representation of all the pixels that form the boundary.
Polyline for lane detection, on the other hand enables autonomous vehicle models to find the correct lane center line and curvatures, and models have an advantage when detecting both since the ground truth is biased toward those geometric characteristics.
Real world industry insights
Autonomous vehicles: Auto manufacturers use polyline annotations for lanes and polygon annotations for vehicles and obstacles as the complete understanding of the shapes is necessary for the vehicles to avoid collisions.
Medical imaging: Radiologists need polygon annotation in computer vision to identify tumors as treatment plans depend upon the accurate delineation of the tumor’s boundaries. Vascular imaging uses polyline annotations to map blood vessels during surgery.
Quality control for manufacturing: Manufacturers use polygons to aid in quality control by identifying defects in products and use polyline annotations to aid in crack identification.
Live video stream annotation for traffic management & road planning
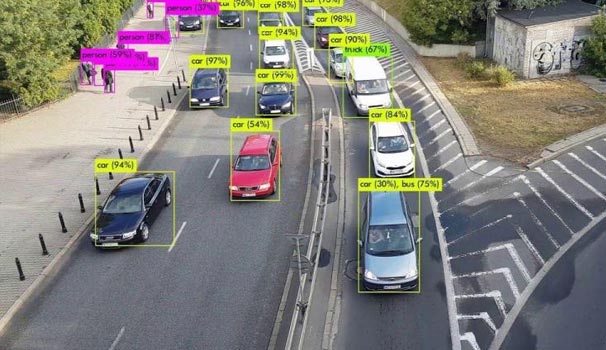
A data analytics firm in San Jose, California was seeking labeled datasets to use Machine Learning (ML) and predict traffic congestion, track vehicle movements, and for urban planning and design. The company struggled to label live and pre-recorded video streams under various traffic and light conditions.
HabileData provided labeling of vehicles, pedestrians and signals on both live and recorded videos using polygon and polyline annotations to record shapes, lanes and movement paths for all objects of interest. Additional labels were applied to categorize, model, color and direction to ensure consistency and high quality frame by frame to provide reliable traffic analysis.
The end results were:
- Sufficient amounts of training data for scalable ML models.
- Dashboards to display real time directional traffic information
- Enhanced data for traffic management and urban planning
How to choose between polygon and polyline annotation
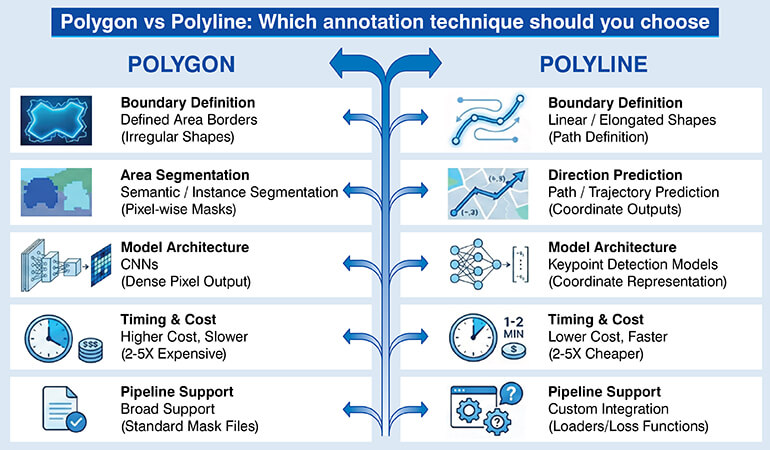
The choice between the types of annotations should be based on an objective comparison of how they affect the labeling process as well as the long term performance of a trained model.
Key decision factors:
- Boundary definition of objects: Polygons are preferred when objects are irregularly shaped. For linear/elongated shapes with large aspect ratios, polylines will better allow you to define the shape of an object.
- Area segmentation vs direction prediction: If you are doing semantic or instance segmentation, then you need polygons because you will need to output pixel-wise masks. When it comes to predicting paths, trajectories, you will want to use polyline annotations since they will require coordinate outputs.
- Model design and architecture: Convolutional neural network architectures used for semantic segmentation expect dense pixel wise label output from polygon annotations. Models designed for detecting keypoints in images operate using polyline like coordinate representations of an object.
- Timing and cost required: Annotations created as polygons are typically 2-5 times more expensive to create per image compared to polyline annotations. It is common for a polygon-annotated object to take 5 times longer to annotate than a polyline annotated object.
- Support by ML pipeline and export format: Confirm that your machine learning pipeline supports the format you are choosing to use. Most frameworks support polygon derived mask files. Some pipelines may require additional steps such as custom data loaders to get polyline formatted coordinates into your model.
Questions that can help teams decide
You can use these diagnostic questions to agree on an annotation strategy:
Does your application require precise boundary detection?
Boundary definition precision is critical when it comes to surgical planning applications. However, lane-keeping assist does not require precise boundary information.
Are target objects thin and linear or area-filling with irregular boundaries?
Polylines are best suited for object identification where the objects have a high aspect ratio. Polygons are better suited for objects that fill areas and have irregular borders.
What is your realistic annotation budget?
If you do not have enough budget to annotate your objects with polygons, then you need to look out for other alternatives such as bounding boxes.
Will your dataset scale to millions of images?
The differences in efficiency between options at large scales will significantly affect long term viability.
The role of quality assurance in polygon & polyline annotation
Combining a multi-level QA process includes having an automated method check for errors such as missing vertices or incorrect orientation of the boundary through scripts that automatically verify geometric properties.
Using two passes of QA has been shown to reduce errors in annotation by up to 60%.
Tools that support advanced annotation workflows have built-in QA capabilities. For example, vertex snapping ensures that edges remain aligned. Providing interpolation suggestions on a batch basis accelerates the annotation process while maintaining consistency.
For any group project where multiple individuals will annotate the same image, use an inter-annotator agreement metric. The inter-annotator agreement metric will highlight areas of inconsistency among the annotators.
Feedback loops between reviewers and annotators that occur at regular intervals help build consistency over time.
Common mistakes teams make when choosing between polygon and polyline annotation
Following are the mistakes that teams commonly repeat in their annotation projects:
- Creating polygon annotations for linear features: This creates extra work for the team without providing extra benefit to the project.
- Insufficiently estimating the amount of time it will take to perform polygon annotations: Estimates are made based on the team’s understanding of what scenes may look like in the real world but do not adequately account for complexity at scale, resulting in delays and excessive costs associated with the project.
- Overuse of polylines in segmentation datasets: Selecting polylines as the most efficient way to perform segmentation when the model needs to segment an area causes a fundamental mismatch.
- Failure to pilot test the selected method prior to going into full scale production: Prior to starting full scale production, you need to validate the method you have selected otherwise the model will need to be completely re-annotated if there are issues encountered during the validation process.
Conclusion
Polygon annotation and polyline annotation are used for different purposes in computer vision, each designed for specific geometric characteristics of an object and the requirements of a model. Polygons allow for detailed segmentation annotations to be performed on area-based objects via capturing their boundaries.
On the other hand, polylines are best suited to represent linear paths or structures and therefore can efficiently be used to represent this type of information.
Therefore, selection between polygon and polyline annotation will depend on the characteristics of the object you want to annotate and the objectives that you have set out for your model. The key is to balance the trade-offs between accuracy versus time and cost.
Strengthen computer vision performance with precise object outlines.
Learn more »
HabileData is a global provider of data management and business process outsourcing solutions, empowering enterprises with over 25 years of industry expertise. Alongside our core offerings - data processing, digitization, and document management - we’re at the forefront of AI enablement services. We support machine learning initiatives through high-quality data annotation, image labeling, and data aggregation, ensuring AI models are trained with precision and scale. From real estate and ITES to retail and Ecommerce, our content reflects real-world knowledge gained from delivering scalable, human-in-the-loop data services to clients worldwide.